我们也都发现了Activity的布局都是通过xml文件来实现的,所以如果你对xml还不是很熟悉,可以到http://www.w3school.com.cn/x.asp上面先学习学习。
如果你已经比较了解了的话,我们来看看下面的各种布局:
LinearLayout的使用方法:
LinearLayout即为线性布局,以垂直或者水平的方法来排列控件。我们来看一个例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <!-- android:id —— 为控件指定相应的ID android:text —— 指定控件当中显示的文字,需要注意的是,这里尽量使用strings.xml文件当中的字符串 android:grivity —— 指定控件的基本位置,比如说居中,居右等位置 android:textSize —— 指定控件当中字体的大小 android:background —— 指定该控件所使用的背景色,RGB命名法 android:width —— 指定控件的宽度 android:height —— 指定控件的高度 android:padding* —— 指定控件的内边距,也就是说控件当中的内容 android:sigleLine —— 如果设置为真的话,则将控件的内容在同一行当中进行显示 --> <TextView android:id="@+id/firstText" android:text="第一行" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:textSize="15pt" android:background="#aa0000" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="10000" android:singleLine="true"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/secondText" android:text="第二行" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:textSize="15pt" android:background="#0000aa" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"/> </LinearLayout> |
效果图如下:
大家可以试着修改里面的属性然后看看具体的效果就会知道这个属性的具体作用!
TableLayout的使用方法:
TableLayout和html里面的table一样,以表格的方法来实现布局。再来看看下面的例子:
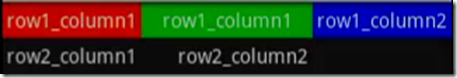
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:stretchColumns="0"> <!-- android:stretchColumns="1"是设置 TableLayout所有行的第二列为扩展列。 也就是说如果每行都有三列的话,剩余的空间由第二列补齐 --> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/row1_column1" android:background="#aa0000" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="@string/row1_column1" android:padding="3dip" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#00aa00" ></TextView> <TextView android:text="@string/row1_column2" android:gravity="right" android:background="#0000aa" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="@string/row2_column1" android:padding="3dip" /> <TextView android:text="@string/row2_column2" android:gravity="right" android:padding="3dip" /> </TableRow> </TableLayout> |
效果如下:
我们再来看看嵌套布局:
比如说一个LinearLayout里面又有另外的一个LinearLayout,并采用不同的布局。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <LinearLayout android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView android:text="red" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#aa0000" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:text="green" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#00aa00" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:text="blue" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#0000aa" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:text="yellow" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:background="#aaaa00" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"/> </LinearLayout> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView android:text="row one" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:text="row two" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:text="row three" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView android:text="row four" android:textSize="15pt" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1"/> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout> |
效果图如下:
当然我们还可以嵌套TableLayout等其他布局。像下面这样的。
以上的布局,有时布局起来可能会相当的麻烦,所以我们可以使用到相对布局:RelativeLayout
先看代码:
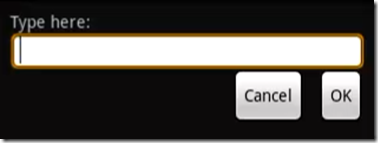
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- android:layout_above 将该控件的底部至于给定ID的控件之上 android:layout_below 将该控件的顶部至于给定ID的控件之下 android:layout_toLeftOf 将该控件的右边缘和给定ID的控件的左边缘对齐 android:layout_toRightOf 将该控件的左边缘和给定ID的控件的右边缘对齐 android:layout_alignBaseline 该控件的baseline和给定ID的控件的baseline对齐 android:layout_alignBottom 将该控件的底部边缘与给定ID控件的底部边缘 android:layout_alignLeft 将该控件的左边缘与给定ID控件的左边缘对齐 android:layout_alignRight 将该控件的右边缘与给定ID控件的右边缘对齐 android:layout_alignTop 将给定控件的顶部边缘与给定ID控件的顶部对齐 android:alignParentBottom 如果该值为true,则将该控件的底部和父控件的底部对齐 android:layout_alignParentLeft 如果该值为true,则将该控件的左边与父控件的左边对齐 android:layout_alignParentRight 如果该值为true,则将该控件的右边与父控件的右边对齐 android:layout_alignParentTop 如果该值为true,则将空间的顶部与父控件的顶部对齐 android:layout_centerHorizontal 如果值为真,该控件将被至于水平方向的中央 android:layout_centerInParent 如果值为真,该控件将被至于父控件水平方向和垂直方向的中央 android:layout_centerVertical 如果值为真,该控件将被至于垂直方向的中央 --> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:padding="10px" > <TextView android:id="@+id/label" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Type here:" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/entry" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@android:drawable/editbox_background" android:layout_below="@id/label" /> <Button android:id="@+id/ok" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/entry" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_marginLeft="10px" android:text="OK" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/ok" android:layout_alignTop="@id/ok" android:text="Cancel" /> </RelativeLayout> |
效果如下:
这样的布局就能更加自由来实现自己想要的效果。
好了,基本的布局就讲到这里,大家还可以查询Android官方的api查看具体的属性。
除非注明,Coder文章均为原创,转载请以链接形式标明本文地址