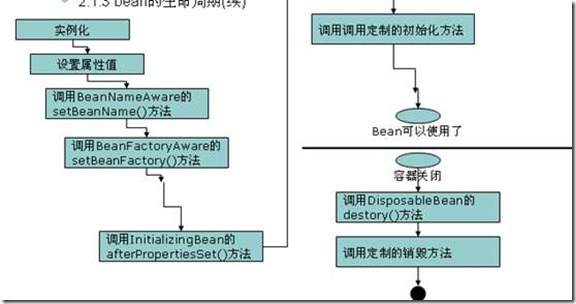
1 实例化(当我们的程序加载beans.xml文件),把我们的bean(前提是scope=singleton)实例化到内存
2 调用set方法设置属性
3 如果你实现了bean名字关注接口(BeanNameAware) 则,可以通过setBeanName获取id号
4 如果你实现了 bean工厂关注接口,(BeanFactoryAware),则可以获取BeanFactory
5 如果你实现了 ApplicationContextAware接口,则调用方法
//该方法传递ApplicationContext
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0)
throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println(“setApplicationContext”+arg0);
}
6 如果bean 和 一个后置处理器关联,则会自动去调用 Object postProcessBeforeInitialization方法
7 如果你实现InitializingBean 接口,则会调用 afterPropertiesSet
8 如果自己在<bean init-method=”init” /> 则可以在bean定义自己的初始化方法.
9 如果bean 和 一个后置处理器关联,则会自动去调用 Object postProcessAfterInitialization方法
10 使用我们的bean
11. 容器关闭
12. 可以通过实现DisposableBean 接口来调用方法 destory
13. 可以在<bean destory-method=”fun1”/> 调用定制的销毁方法
小结: 我们实际开发中往往,没有用的这么的过程,常见的是:
1->2->6->10->9->11
以下为验证代码:
PersonService.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 | package com.lpq.beanlife; import javax.annotation.PostConstruct; import javax.annotation.PreDestroy; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware; import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean; import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; public class PersonService implements BeanNameAware,BeanFactoryAware,ApplicationContextAware,InitializingBean,DisposableBean{ private String name; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { System.out.println("setName........."); this.name = name; } public void sayHi(){ System.out.println("hi "+name); } //也可以通过注解的方式来配置哪个方法是init-method @PostConstruct public void init(){ System.out.println("init........."); } @PreDestroy public void mydestroy(){ System.out.println("mydestroy.........."); } public PersonService(){ System.out.println("PersonService......start"); } //该方法可以给arg0表示正在被实例化的bean id @Override public void setBeanName(String arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("setBeanName.....id:"+arg0); } //该方法可以传递beanfactory @Override public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory arg0) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("setBeanFactory....."+arg0); } //该方法传递ApplicationContext @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext arg0) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("setApplicationContext.........."+arg0); } @Override public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("afterPropertiesSet........."); } @Override public void destroy() throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //我们可以关闭数据链接 socket 文件流 释放资源 System.out.println("destroy.........."); } } |
bean.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | <bean id="person" init-method="init" destroy-method="mydestroy" class="com.lpq.beanlife.PersonService"> <property name="name"> <value>小明</value> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置我们自己的后置处理器(有点类似我们的filter) --> <bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.lpq.beanlife.MyBeanPostProcessor"></bean> |
MyBeanPostProcessor.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | package com.lpq.beanlife; import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor; public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor { @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization........."); System.out.println(arg0+"被创建的时间是"+new Date().toLocaleString()); return arg0; } @Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object arg0, String arg1) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization........."); return arg0; } } |
App.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 | package com.lpq.beanlife; import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource; public class App { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("com/lpq/beanlife/beans.xml"); PersonService ps = (PersonService)ac.getBean("person"); ps.sayHi(); System.out.println("-------------------------"); BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(new ClassPathResource("com/lpq/beanlife/beans.xml")); factory.getBean("person"); } } |
问题:通过BeanFactory来获取bean对象,bean的生命周期是否和Applicationcontext 是一样吗?
不是一样的,bean是工厂中创建的生命周期会简单一些:
除非注明,Coder文章均为原创,转载请以链接形式标明本文地址